Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein.
Topic Contents
Breast Implant Surgery for Breast Reconstruction
Breast implants re-create the shape of a breast after part or all of the breast is removed (mastectomy) because of cancer. Several types of implants are available.
Sometimes an implant is placed during the same surgery as mastectomy. But often you will have two surgeries. The doctor will first place a tissue expander beneath the skin. Saline is gradually added to the expander to help stretch the skin. This may take several months. When the right size is reached, the expander is taken out and an implant is put in. The nipple and the darker area around it (areola) are created at a later time.
After surgery, you will probably go home the same day or the next day. Many people can go back to work or their usual routine in 3 to 6 weeks.
Your new breast will likely not have any feeling. It will also look different than before.
How It Is Done
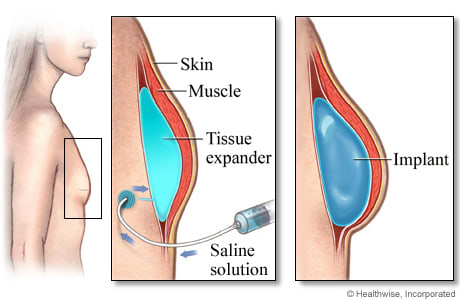
To place an implant after mastectomy, the surgeon will use the same incision that was used to remove the breast tissue. The implant may be placed directly under the skin, but it is usually put under the chest muscle.
Often, before an implant is placed, a doctor will first place a balloon (or tissue expander) beneath the chest muscle. Saline is added to the expander every 1 to 2 weeks to help stretch the skin and muscle. This may take several months. When the muscle and skin are stretched enough, the expander is taken out and an implant is put in.
What To Expect
When you wake up from surgery, you will have bandages over the surgery sites. You may wear a special bra that holds your bandages in place. You may have drainage tubes to collect fluid and keep it from building up around the surgery site.
If the implant was placed at the same time as your mastectomy, you may stay in the hospital for 1 or 2 days. If the implant is placed later, you will probably be able to go home the same day.
Most people have soreness, redness, and swelling in the breast after implant surgery. You may need pain medicine for a week or two. Your doctor will give you instructions on how to care for your incision. Your doctor may also prescribe antibiotics to help prevent infection.
You may be able to go back to work or your usual routine in 3 to 6 weeks or sooner. Most people need to avoid strenuous activity for several weeks.
Why It Is Done
Breast implant surgery can be done to restore the appearance of a breast after mastectomy. It may also be done for people who have problems with breast development.
Breast reconstruction may help a person feel better about their appearance. Some people say it helps them feel better about their bodies and have better mental and sexual well-being.
How Well It Works
Breast implants work best for people who have small- to medium-sized breasts or for people who have both breasts removed (bilateral mastectomy).
Compared to tissue flap surgery for breast reconstruction, breast implant requires a shorter surgery and has a quicker recovery time.
A breast implant will likely need to be replaced at some point. Some implants have lasted 20 to 30 years, but that is not common. This means that someday you will probably need to have surgery to replace the implant.
Risks
Many of the risks associated with breast reconstruction are the same as those with any surgery: infection, poor wound healing, bleeding, or a reaction to the anesthesia used in surgery.
Other risks from breast implants include:
- Capsular contracture. It occurs when scar tissue around the implant hardens and begins to squeeze the implant. Surgery may be needed to remove the scar tissue or replace the implant.
- Changes in the implant. Normal activity or an injury to the breast can damage the implant, causing it to leak, deflate, or rupture. Over time, the implant may harden, develop ripples, shift position, or change shape. Surgery may be needed to remove the implant and replace it if any of these changes occur.
- Results that don't look perfect.
- Uneven breasts. Breasts with implants don't sag with age like natural breasts. This could be a problem if you just have one breast implant.
- Silicone implants that leak. Silicone implants can leak inside the body without causing any symptoms.
- A small risk of getting cancer. Breast-implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL) is a serious cancer that develops near the implant and can lead to death. The risk of getting this cancer seems to be higher for breast implants with a textured surface than for implants with a smooth surface.
Some people are at higher risk for problems from surgery. This includes those who:
- Have obesity.
- Have high blood pressure.
- Have diabetes.
- Smoke.
- Are in poor health.
Credits
Current as of: October 1, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: October 1, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com.
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.